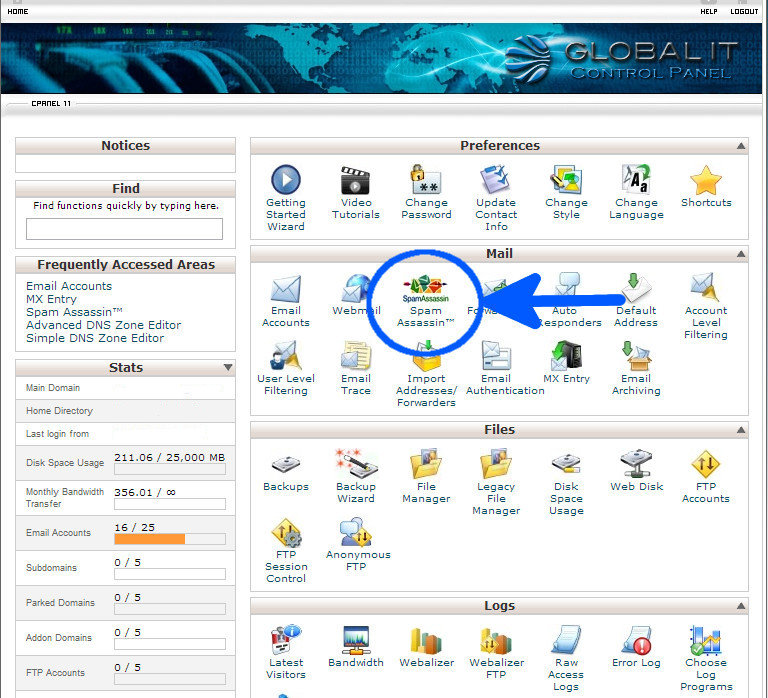
Spyware and Adware are programs that are installed on a computer that perform operations that the user probably doesn’t want. Spyware is a program that was created for the purpose of collecting information and sending it to a designated entity. The information it gathers can be from which terms or phrases you are searching and which websites you are visiting, to personal and financial information like your date of birth, social security number, or credit card information. Adware has a different purpose. It will usually ‘pop-up’ advertisements in websites when you search for a specific term or phrase, or it may be an entirely separate pop-up window on your desktop that advertises something.
Spyware and Adware are programs that are installed on a computer that perform operations that the user probably doesn’t want. Spyware is a program that was created for the purpose of collecting information and sending it to a designated entity. The information it gathers can be from which terms or phrases you are searching and which websites you are visiting, to personal and financial information like your date of birth, social security number, or credit card information. Adware has a different purpose. It will usually ‘pop-up’ advertisements in websites when you search for a specific term or phrase, or it may be an entirely separate pop-up window on your desktop that advertises something.
Now you may be thinking: “Who would install such a program?” The answer is: “More than you would think.” These programs are typically installed without the knowledge of the user. They are usually packaged together with other ‘free software’ downloaded from the internet. Think of the phrase “nothing in life is free.” This holds true for computer software. If you got it for free, there is a big chance the creator is making money somehow. Often it’s by accepting payment from companies in return for adding these programs to their ‘free software’.
Here are some identifiers that may indicate your computer is infected:
- Your computer is slowing significantly
- You are redirected to a different website than the one you entered
- You get random informational or advertising pop-ups
- Your internet connection seems very slow or stops working
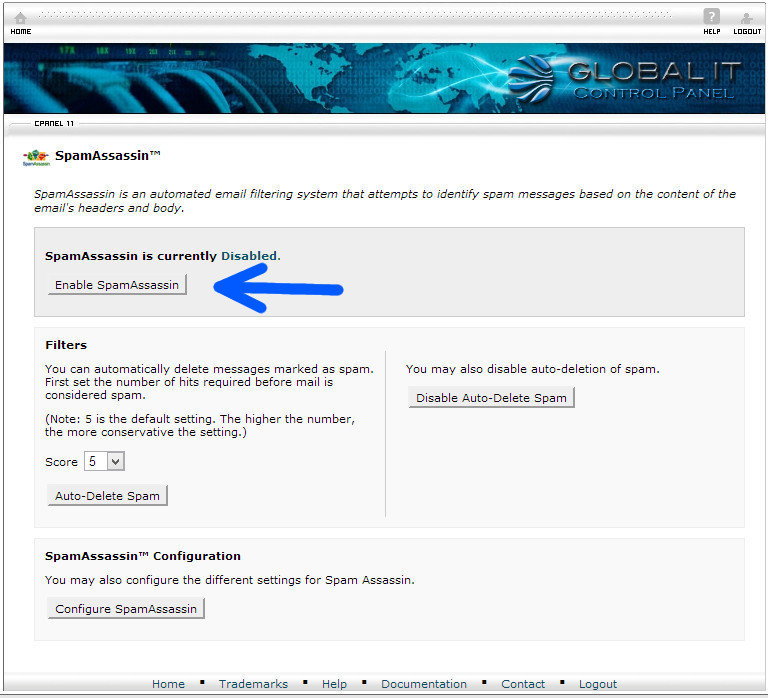
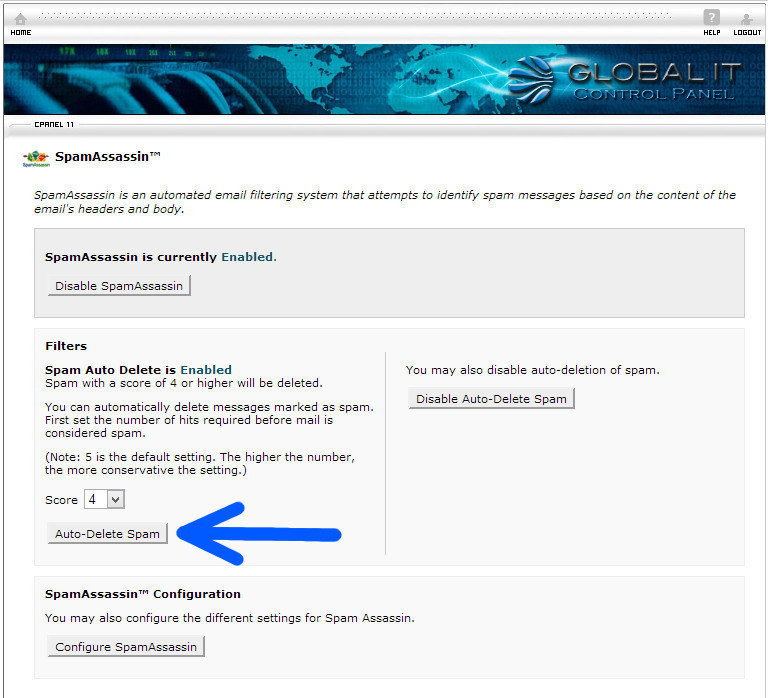
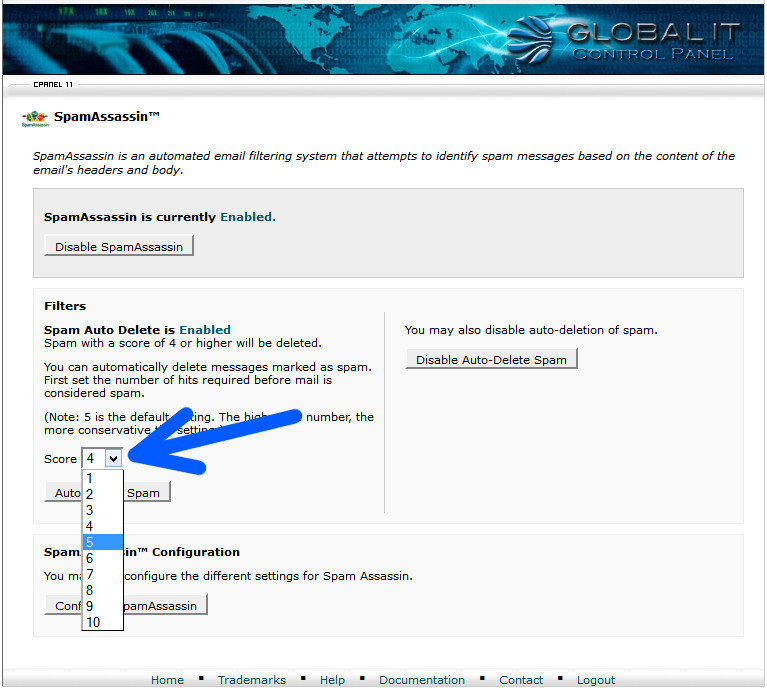
There are some things you can do to prevent the installation of these programs. Some software has the option of ‘Customized Installation’ which allows you to deselect the spyware or adware program from being installed. Another way is to read the ‘Agreement’ for any indication that these programs are included, granted they are being honest in disclosing that in addition to their program, other ‘alternate’ or ‘third party applications will be installed. However, these methods do not guarantee that you won’t have spyware or adware installed. Many programs may not disclose this or the program will not function without it. Sometimes these programs can be installed by visiting an unreliable website.
The only surefire way to avoid having spyware and/or adware being installed on your computer is to only install trusted software from trusted sources, and visit only trusted websites. Trusted companies like Apple, Microsoft, Adobe, and others do not include these programs in their installation packages. More and more methods are being developed to deploy these unwanted programs.
If you suspect your computer contains spyware or adware, use a special program to find and remove these unwanted programs. Some reliable programs that are highly recommended are Ad-aware and Spybot. Remember though, some spyware and adware programs might have already done some damage to your computer that may require a qualified technician to repair. Global IT, a leader in internet security, staffs certified technicians that can restore your computer back to a level of optimal performance.
https://info.globalit.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/Spyware-adware.jpg
Internet Security|Webmaster